Mirror Formula and Magnification
Mirror Formula and Magnification: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Relation between Radius of Curvature and Focal Length of a Spherical Mirror, Magnification in Curved Mirror,Co-ordinate Convention and Mirror Formula etc.
Important Questions on Mirror Formula and Magnification
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 50 cm. A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and the plane mirror is 30 cm, it is found that there is no gap between the images formed by the two mirrors. The radius of the convex mirror is:
A large temple has a depression in one wall. On the floor plan, it appears as an indentation having a spherical shape of radius . A worshipper stands on the centreline of the depression, out from its deepest point, and whispers a prayer. Where is the sound concentrated after reflection from the black wall of the depression?
Where should an object long be placed in front of a convex mirror of focal length to obtain an image long.
A concave mirror has a focal length of . Determine the position of the object for which an erect and four times the size of the object image is formed. Draw relevant ray diagram.
Shilpi places a spherical mirror of radius in glycerine. Its focal length in air and glycerine differ by _____.
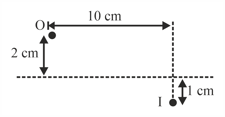
The principal axis of a spherical mirror is shown by dotted line. is the point object whose real image is . Find the distance of the pole and centre of curvature of the mirror from object measured along principal axis by drawing ray diagram.
What is the difference between longitudinal and transverse magnification?
A car of length inch moves at a constant velocity . A man wants to take a photo of side view of the car. The size of the image of the car is long. The time of exposure needed for the car to get a clear picture, if the image should not move more than , is
(i) Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is .
(ii) A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an object placed at in front of it. Where is the image located?
The ratio of distance of an object to the distance of image formed by a convex mirror is . Calculate the ratio of distance of image from the mirror to the focal length of the mirror.
If the focal-length of a spherical mirror is . Find its radius of curvature.
Which of the following points of a spherical mirror is taken as origin in case of measurement of concerning distance.
Identify the correct statement:
If the radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. Then its focal length is equal to_____.
The relation between focal length(f) and radius of curvature(R) of a spherical mirror is_____.
A convex mirror used for rear-view on an automobile has a radius of curvature of . If a bus is located at from this mirror, What will be the position of image.
For a concave mirror of focal length to form twice magnified image, distance of object from its pole is/are
The magnification produced by a spherical mirror and a spherical lens is Then:
The object distance , image distance and focal length for a spherical mirror are related as
The ratio of the focal length of spherical mirror to its radius of curvature is
